Mastering Osterwalder’s Business Model Canvas: A Guide for Startups
If you’re an entrepreneur with a solid business idea, the next crucial step is structuring your concept for success. Alexander Osterwalder’s Business Model Canvas is an excellent tool for this, providing a clear framework to organize and refine your business strategy. This article dives into the key elements of the Business Model Canvas, showcases practical examples, and offers a step-by-step guide on applying it to your startup.
What is the Business Model Canvas?
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic template that breaks down your business model into nine interconnected components. This visual chart helps you understand, design, and innovate your business model. Here’s a closer look at each component, starting with the value proposition, the core of your business idea.
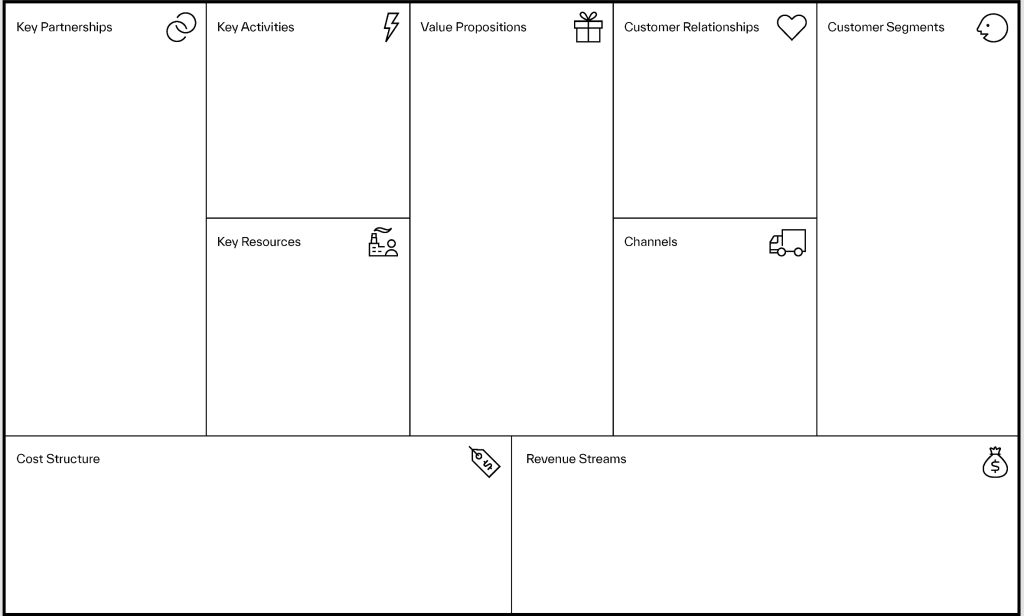
Value Propositions: The Heart of Your Business
Your value proposition is what sets your business apart. It answers the question: What unique value are you offering to your customers? To define this, consider the problems you’re solving and the needs you’re fulfilling. For example:
- Unique Product Features: What specific benefits do your products or services offer that competitors don’t?
- Cost Reduction: How does your product help customers save money?
- Customization: How does your product or service cater to individual customer needs?
- Convenience: How does your solution simplify the customer’s life?
Example: Dropbox
- Value Proposition: Easy, secure, and accessible file storage and sharing for individuals and businesses.
- Problems Solved: Eliminates the need for physical storage, reduces risk of data loss, and simplifies file sharing.
Customer Segments: Who Are You Serving?
Identify the specific groups of people or organizations your business aims to reach and serve. Understanding your customers’ needs, behaviors, and demographics is vital. Some key questions to ask include:
- Who are our most important customers?
- What are their characteristics and preferences?
- How do they currently solve the problem you’re addressing?
Example: Airbnb
- Customer Segments: Travelers seeking unique, affordable accommodations; homeowners wanting to rent out their spaces.
- Customer Needs: Affordable travel options, income generation for property owners.
Channels: How Will You Reach Your Customers?
Define the various ways you will deliver your value proposition to your customer segments. This includes both direct and indirect channels, such as:
- Online Platforms: Websites, mobile apps, social media.
- Physical Locations: Stores, pop-up shops.
- Partnerships: Third-party distributors, affiliates.
Example: Amazon
- Channels: Website, mobile app, Amazon Prime, third-party logistics.
Customer Relationships: Building Connections
Determine the type of relationship you want to establish with each customer segment. Relationships can range from personalized services to automated interactions. Consider:
- How do you acquire customers?
- How do you retain customers?
- How do you grow your customer base?
Example: Spotify
- Customer Relationships: Personalized playlists, social sharing features, customer support.
Revenue Streams: Generating Income
Identify how your business will earn revenue from each customer segment. Revenue streams can include:
- Direct Sales: Selling products or services directly to customers.
- Subscription Fees: Charging customers a recurring fee for access to a product or service.
- Advertising: Earning revenue from third-party advertisements.
Example: Netflix
- Revenue Streams: Subscription fees from individual users, partnerships with content creators.
Key Resources: What Do You Need?
List the critical assets your business requires to function effectively. This includes physical, intellectual, human, and financial resources.
Example: Google
- Key Resources: Search algorithms, data centers, brand, user data.
Key Activities: What Will You Do?
Identify the most important tasks your business must perform to deliver its value proposition. Key activities might include:
- Production: Manufacturing products, creating content.
- Problem Solving: Providing customer support, consulting.
- Platform Management: Maintaining and updating software platforms.
Example: Uber
- Key Activities: Platform maintenance, driver management, customer support.
Key Partnerships: Who Will Help You?
Consider the external companies or individuals you need to partner with to make your business model work. These might include suppliers, strategic alliances, or joint ventures.
Example: Apple
- Key Partnerships: Component suppliers, app developers, telecom providers.
Cost Structure: Managing Expenses
Analyze the major costs involved in operating your business model. This includes fixed and variable costs, economies of scale, and cost optimization strategies.
Example: Tesla
- Cost Structure: Manufacturing, R&D, marketing, distribution.
Applying the Business Model Canvas to Your Startup
Step 0: Get a Head Start with Automated Business Model Canvas
Want to save time and ensure accuracy? Start with an automatically generated Business Model Canvas based on your website. Our service analyzes your existing online presence and provides a ready-made canvas, giving you a solid foundation to build on. Try our automated Business Model Canvas service now and get a head start in structuring your business model.
Step 1: Start with Your Value Proposition
Clearly define what unique value your startup offers. This is the cornerstone of your business model.
Step 2: Identify Your Customer Segments
Pinpoint the specific groups of people or organizations you aim to serve. Tailor your value proposition to meet their needs.
Step 3: Establish Your Channels
Determine the best ways to reach your customer segments and deliver your value proposition.
Step 4: Define Customer Relationships
Decide on the nature of relationships you want to build with your customers, and plan how to acquire, retain, and grow your customer base.
Step 5: Outline Revenue Streams
Identify all potential revenue sources and determine how each will contribute to your overall income.
Step 6: Determine Key Resources
List all essential resources your business needs to operate and deliver value to your customers.
Step 7: Identify Key Activities
Outline the crucial tasks your startup must perform to succeed.
Step 8: Form Key Partnerships
Identify the external partners that will help you achieve your business objectives.
Step 9: Analyze Cost Structure
Understand the costs involved in your business model and develop strategies to manage them efficiently.
Conclusion
Using the Business Model Canvas, you can transform your business idea into a structured, comprehensive plan. This tool helps you visualize each component of your business, ensuring that all aspects are aligned and geared towards delivering value to your customers. By following this guide, you can effectively apply the Business Model Canvas to your startup, setting the foundation for a successful and sustainable business.
For a more detailed, customized analysis, try our Business Model Canvas Conversion Service. Sign up today to convert your website into a comprehensive Business Model Canvas and set your startup on the path to success!