Authors: Gleb Mezentsev, Danil Gusak, Ivan Oseledets, Evgeny Frolov
Published on: September 27, 2024
Impact Score: 7.8
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2409.18721
Summary
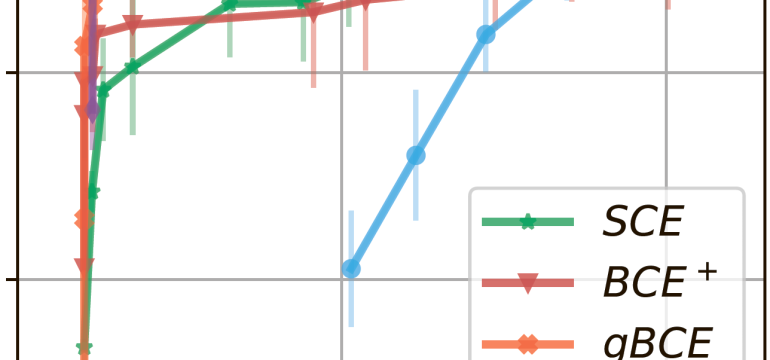
- What is new: A novel Scalable Cross-Entropy (SCE) loss function for recommender systems that is more efficient in terms of time and memory usage.
- Why this is important: High computational overload and excessive GPU memory usage in modern recommender systems when dealing with large item catalogs.
- What the research proposes: Introducing SCE loss function that approximates CE loss using a selective GPU-efficient computation strategy without compromising recommendation quality.
- Results: SCE significantly reduces peak memory usage by up to 100 times while retaining or even improving recommendation performance metrics.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Selective GPU-efficient computation strategy
Models used: SCE loss function approximates softmax distribution through maximum inner product search
Data used: Multiple datasets with large-size catalogs
Potential Impact
Companies operating large recommender systems and those developing large-scale models, such as large language models, could benefit significantly from these insights.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: EffiRecom.


Leave a Reply