Authors: Hartmut Häntze, Lina Xu, Felix J. Dorfner, Leonhard Donle, Daniel Truhn, Hugo Aerts, Mathias Prokop, Bram van Ginneken, Alessa Hering, Lisa C. Adams, Keno K. Bressem
Published on: May 10, 2024
Impact Score: 7.6
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2405.06463
Summary
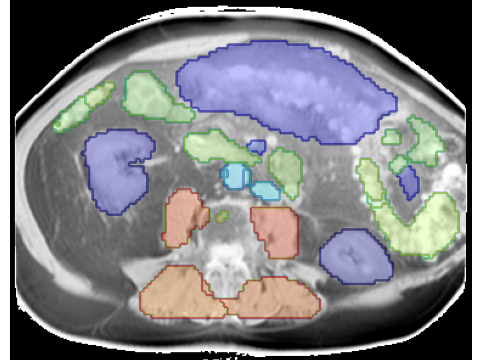
- What is new: Introduces a deep learning model for multi-organ segmentation in MRI scans that leverages cross-modality learning from CT scans for enhanced accuracy.
- Why this is important: Current MRI analysis faces limitations due to resolution challenges, lack of standardized intensity values, and variability in sequences.
- What the research proposes: A deep learning model trained on a large dataset of MRI and CT scans, using cross-modality transfer learning and human-in-the-loop annotation workflows for optimized segmentation of multiple organs.
- Results: High segmentation accuracy for well-defined organs with DSC scores up to 0.97 for lungs and 0.95 for the heart, but lower accuracy for smaller structures, indicating room for model improvement.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Deep learning, cross-modality transfer learning
Models used: Not specified
Data used: 1,200 UK Biobank MRI scans, 221 in-house MRI scans, 1228 CT scans
Potential Impact
Healthcare imaging, radiology software providers, medical research organizations
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: InsightAI.

Leave a Reply