Authors: Bansi Mandalia, Steve Greenwald, Simon Shaw, Gregory Slabaugh
Published on: April 09, 2024
Impact Score: 7.4
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2404.15336
Summary
- What is new: An ensemble model combining k-Nearest Neighbours and Random Forest for predicting the source of occlusion in arteries is introduced.
- Why this is important: The need for a non-invasive method to detect coronary artery disease (CAD) by identifying partial occlusions in coronary arteries.
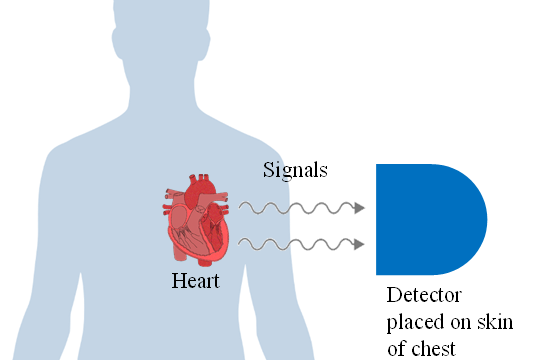
- What the research proposes: Using machine learning to predict the source of arterial occlusion from data simulating acoustic signals at the chest surface caused by changes in blood flow.
- Results: The ensemble model of k-Nearest Neighbours and Random Forest outperformed other algorithms in accuracy, as measured by mean squared error and Euclidean distance.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: nan
Models used: k-Nearest Neighbours, Random Forest, Ensemble Model
Data used: Simulated surface signals data from randomly assigned source positions
Potential Impact
Healthcare diagnostics, Wearable health tech, Medical imaging software companies
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: CardioSound.

Leave a Reply