Authors: Clément Christophe, Praveen K Kanithi, Prateek Munjal, Tathagata Raha, Nasir Hayat, Ronnie Rajan, Ahmed Al-Mahrooqi, Avani Gupta, Muhammad Umar Salman, Gurpreet Gosal, Bhargav Kanakiya, Charles Chen, Natalia Vassilieva, Boulbaba Ben Amor, Marco AF Pimentel, Shadab Khan
Published on: April 23, 2024
Impact Score: 7.8
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2404.14779
Summary
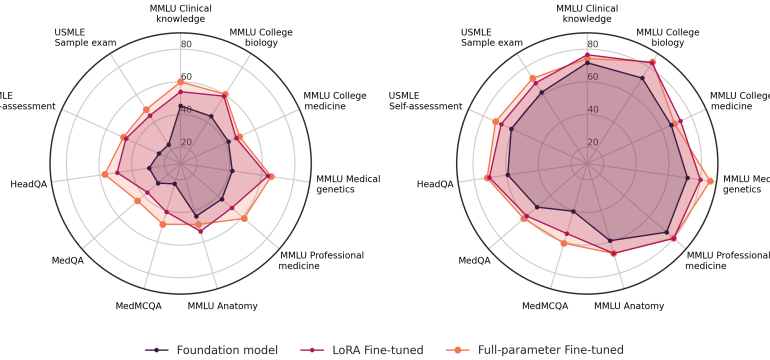
- What is new: The study introduces Med42, a medical Large Language Model (LLM) with enhanced retrieval, reasoning, and question-answering capabilities, achieving a 72% accuracy on USMLE datasets.
- Why this is important: Identifying the most effective fine-tuning methodology for medical LLMs to improve knowledge retrieval and question-answering capabilities.
- What the research proposes: Comparative analysis of full-parameter fine-tuning and parameter-efficient tuning on LLMs specifically designed for the medical field.
- Results: Med42 sets a new performance standard for medical LLMs with its high accuracy rate on well-known medical benchmarks.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Llama-2 architecture
Models used: Developed and refined series of LLMs specifically for medical applications
Data used: USMLE datasets and various medical benchmarks
Potential Impact
Healthcare providers, medical education platforms, and AI-driven healthcare application developers
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: MediMind.


Leave a Reply