Authors: Paul Maximilian Röhrig, Nancy Radermacher, Luis Böttcher, Andreas Ulbig
Published on: April 22, 2024
Impact Score: 8.0
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2404.14371
Summary
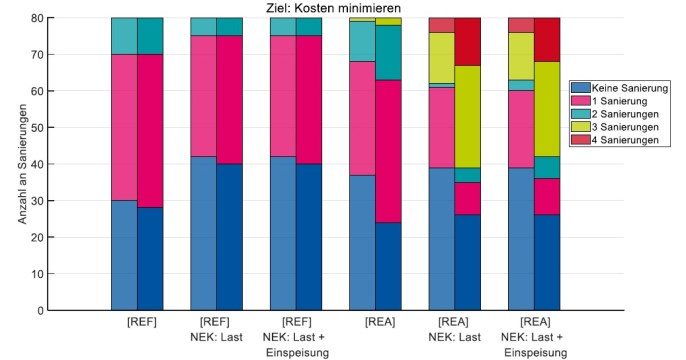
- What is new: This research introduces an innovative method that combines multi-criteria optimization for building-level decisions with grid expansion analysis to understand their reciprocal effects on decentralized energy supply systems aimed at decarbonizing the building sector.
- Why this is important: The need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the building sector by 2045, considering the challenges of integrating renewable energy sources and low-CO2 heat generators without overburdening the electrical grid infrastructure.
- What the research proposes: A holistic analysis method that merges building-level expansion and operation decision-making with grid expansion planning to assess the impact of increased self-generation and renewable energy adoption on grid stability and charges.
- Results: The study provides insights into how grid charges and expansion influence the decision-making of grid users towards adopting renewable energy solutions, thereby suggesting a pathway to decentralized energy systems without overloading the grid.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Multi-criteria optimization combined with grid expansion determination approaches.
Models used: Decentralized energy supply models with emphasis on self-generation and renewable energy integration.
Data used: Historical data on building energy consumption, grid load, and capacity for renewable energy generation.
Potential Impact
Utility companies, renewable energy solution providers, and companies involved in building energy retrofit services could significantly benefit or need to adapt based on these insights.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: GridFlex Solutions.

Leave a Reply