Authors: Madeleine Pollack, Ryan Piansky, Swati Gupta, Alyssa Kody, Daniel Molzahn
Published on: April 17, 2024
Impact Score: 8.0
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2404.11520
Summary
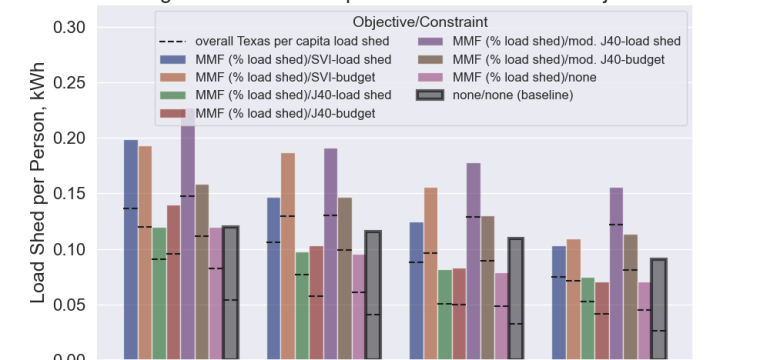
- What is new: This research reveals that the current methods of allocating funds to de-risk power lines under the Justice40 and SVI indices are insufficient in reducing power outages in indigenous communities and areas with high wildfire risks.
- Why this is important: Wildfires ignited by power system infrastructures pose a significant risk, and emergency power shutoffs impact vulnerable communities.
- What the research proposes: Proposes a method to equitably allocate funds to underground power lines, adding group-level protections to ensure fair distribution of load shedding.
- Results: The proposed method shows potential in correctly allocating resources to protect against wildfires, particularly in indigenous communities and high-risk areas, which were previously neglected.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Uses a high-fidelity synthetic power grid dataset, simulating the Texas transmission system.
Models used: Comparison of budget allocation models based on the Justice40 initiative and the Social Vulnerability Index (SVI).
Data used: Synthetic power grid data, Justice40 index, and the CDC’s Social Vulnerability Index (SVI).
Potential Impact
Utility companies in wildfire-prone regions, infrastructure development sectors, and governmental or non-governmental organizations focused on disaster mitigation.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: EquiGrid.

Leave a Reply