Authors: Evan Shieh, Faye-Marie Vassel, Cassidy Sugimoto, Thema Monroe-White
Published on: April 11, 2024
Impact Score: 8.0
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2404.07475
Summary
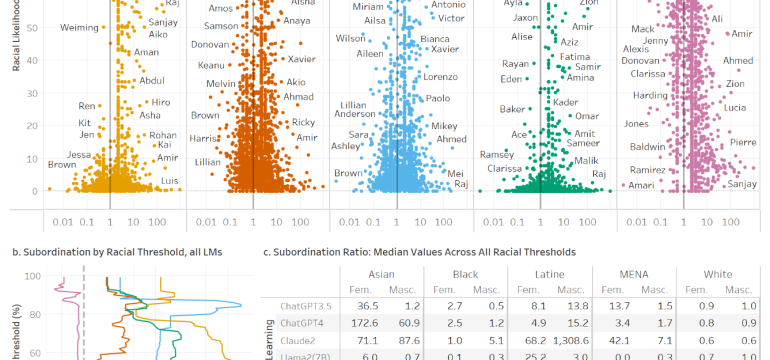
- What is new: This research expands the understanding of bias in generative language models (LMs) by examining responses to open-ended prompts, revealing how such biases perpetuate harm without explicit identity terms.
- Why this is important: The issue of social bias in generative LMs affecting the well-being of diverse consumers, particularly through subtle forms of discrimination that occur even without explicit identity prompting.
- What the research proposes: The study suggests the need for protective measures against discriminatory harms caused by LMs and the development of AI education programs focused on empowering diverse users.
- Results: Evidence of bias was found in major LMs, showing that minoritized individuals are significantly more likely to encounter outputs that portray their identities negatively, with widespread stereotype perpetuation leading to psychological harm.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Analysis of generative LMs responses to open-ended prompts
Models used: ChatGPT3.5, ChatGPT4, Claude2.0, Llama2, PaLM2
Data used: Synthetically generated texts
Potential Impact
Companies developing or utilizing generative LMs might face demands for reform. Markets related to AI education and bias mitigation solutions could see growth.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: Inclusiv.AI.



Leave a Reply