Authors: Yu Zhang, Haozhe Wang, Jie Cui, Tao He, Gaote Qiu, Yu Xu, Jing Zhang
Published on: March 29, 2024
Impact Score: 7.4
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2403.20019
Summary
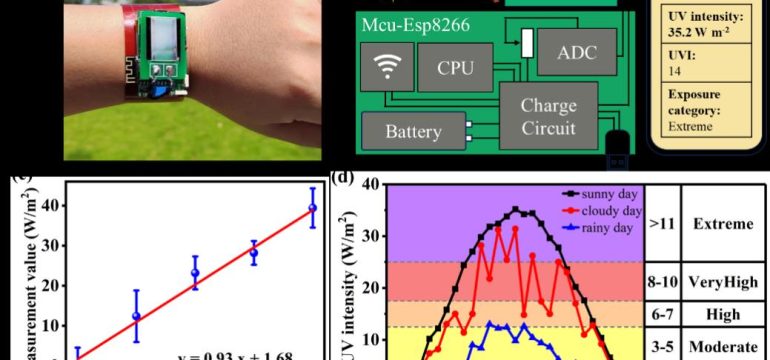
- What is new: A wearable real-time UV photodetector based on hydrogenated titanium dioxide film prepared using a novel, rapid, and low-cost method.
- Why this is important: The need for a simple, rapid, and low-cost method for preparing UV photodetectors for real-time monitoring.
- What the research proposes: Using radio frequency atmospheric pressure plasma to synthesize hydrogenated titanium dioxide film, enhancing its conductivity significantly.
- Results: Achieved a conductivity of 10.2 S cm$^{-1}$, with the film showing high responsivity in the UV range and effective real-time UV monitoring when integrated into a wearable sensor.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Radio frequency atmospheric pressure plasma for film synthesis.
Models used: First-principles calculations for understanding the impact of oxygen vacancies on the lattice structure.
Data used: Measurements of conductivity, responsivity, and real-time monitoring effectiveness.
Potential Impact
This technology could disrupt the wearable tech market, particularly in health and environmental monitoring sectors, benefiting companies specializing in UV monitoring devices.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: UVigilant.

Leave a Reply