Authors: Justin B. DeMonte, Bonnie E. Shook-Sa, Michael G. Hudgens
Published on: March 26, 2024
Impact Score: 7.4
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2403.18115
Summary
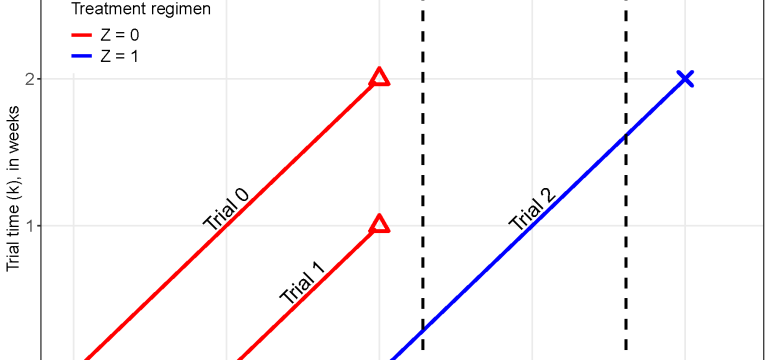
- What is new: Introduction of a new NTE inverse probability weighted estimator that accounts for effectiveness variability over time and against emerging variants.
- Why this is important: Previous methods of estimating COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness using observational data may not account for changes over time or against new variants, leading to biased results.
- What the research proposes: A sequence of nested trials using an inverse probability weighted estimator is proposed to better estimate vaccine effectiveness that may vary with time and against different virus strains.
- Results: The proposed method was applied to data from over 120,000 residents in Abruzzo, Italy, providing nuanced insights into the vaccine’s effectiveness throughout 2021.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: nan
Models used: Nested trial emulation (NTE), inverse probability weighting
Data used: Observational data from over 120,000 residents of Abruzzo, Italy during 2021
Potential Impact
Healthcare policymakers, vaccine developers, and public health organizations could leverage these insights for more targeted vaccine distribution and development strategies.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: EpiTrack.

Leave a Reply