Authors: Zhenrui Yue, Huimin Zeng, Yimeng Lu, Lanyu Shang, Yang Zhang, Dong Wang
Published on: March 22, 2024
Impact Score: 7.8
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2403.14952
Summary
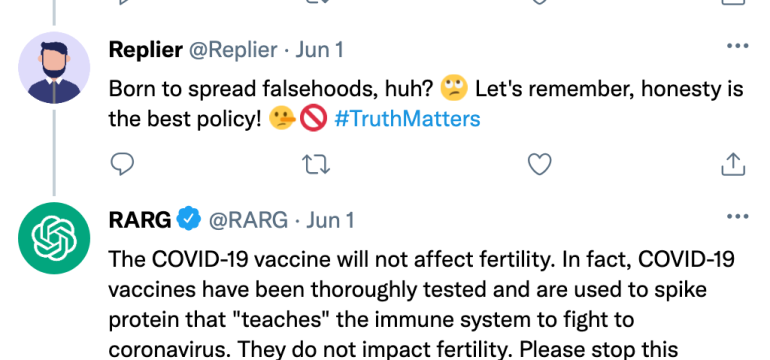
- What is new: The research introduces a retrieval augmented response generation method (RARG) that uses scientific sources to counter online misinformation, focusing on the improvement of text quality and reduction of repetitive responses.
- Why this is important: The rise of online misinformation threats and the ineffective, often impolite or unfactual user responses.
- What the research proposes: A two-stage approach called RARG that first collects evidence from a large database of academic articles, then uses large language models refined with reinforcement learning to generate polite and factual counter-misinformation responses.
- Results: In tests related to COVID-19 misinformation, RARG generated responses of noticeably higher quality than existing methods, as assessed in terms of politeness, factual accuracy, and relevance.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: RARG with a retrieval-augmented component for evidence collection, and reinforcement learning for response generation
Models used: Large Language Models (LLMs)
Data used: Over 1M academic articles database for evidence retrieval
Potential Impact
Social media platforms, news organizations, and educational tech companies might strongly benefit or need to adapt to these findings by incorporating such technologies to fight misinformation.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: FactsMatterAI.


Leave a Reply