Authors: Ziya Ata Yazıcı, İlkay Öksüz, Hazım Kemal Ekenel
Published on: March 15, 2024
Impact Score: 7.6
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2403.09942
Summary
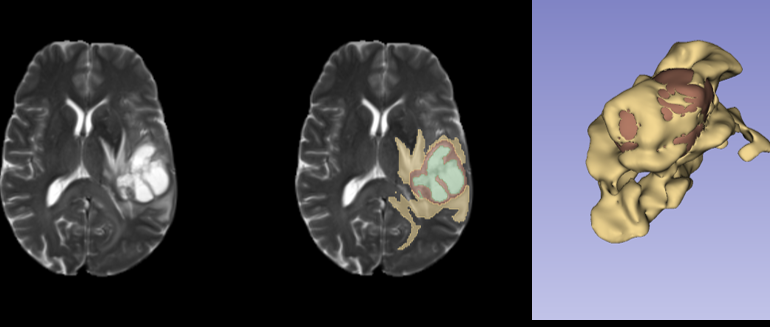
- What is new: A new multi-scale, attention-guided hybrid U-Net-shaped model called GLIMS is introduced for 3D brain tumor segmentation.
- Why this is important: Glioblastoma is hard to diagnose early due to its varied appearance, and existing automated detection methods struggle with this heterogeneity.
- What the research proposes: GLIMS uses multi-scale feature extraction, Swin Transformer blocks for improved global feature extraction, and attention-guided segmentation mask generation with hierarchical supervision.
- Results: The model achieved 92.19, 87.75, and 83.18 Dice Scores for Whole Tumor, Tumor Core, and Enhancing Tumor regions, respectively, on the validation set.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Multi-scale, attention-guided hybrid U-Net-shaped architecture
Models used: Swin Transformer
Data used: Clinically acquired MRI data from the BraTS challenge
Potential Impact
Healthcare and medical imaging companies, particularly those involved in brain tumor diagnosis and treatment, might see significant benefits or disruption from the adoption of GLIMS.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: NeuroAID.
Leave a Reply