Authors: Touchchai Chotisorayuth, Andreas Tiffeau-Mayer
Published on: March 14, 2024
Impact Score: 8.0
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2403.09010
Summary
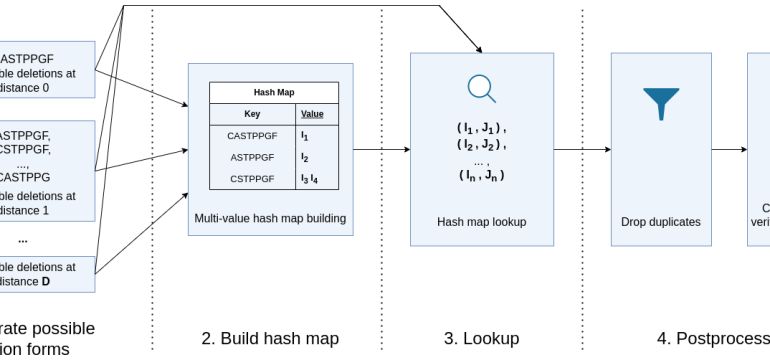
- What is new: The introduction of XTNeighbor, a scalable and massively parallelizable algorithm, for identifying AIR sequences with similar functions based on sequence similarity.
- Why this is important: The challenge of efficiently identifying adaptive immune receptor (AIR) sequences with similar functions from a vast diversity of receptor-antigen pairs, which is crucial for understanding immune system history from genomic data.
- What the research proposes: Using a symmetric deletion lookup approach, enhanced by the novel XTNeighbor algorithm, to perform radius-based searches for Levenshtein neighbors, enabling rapid identification of functionally similar AIR sequences.
- Results: XTNeighbor can identify all sequence neighbors differing by up to two edits for one million input sequences in seconds on commodity hardware, significantly outperforming existing methods.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Symmetric deletion lookup, massively parallelized computations on GPUs
Models used: nan
Data used: Large-scale immunosequencing data
Potential Impact
Biotech and pharmaceutical companies engaged in immunotherapy development, genetic research organizations, and health data analytics companies could greatly benefit from the application of these insights.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: ImmunoMatch.

Leave a Reply