Authors: Michael Howard
Published on: March 07, 2024
Impact Score: 7.8
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2403.04935
Summary
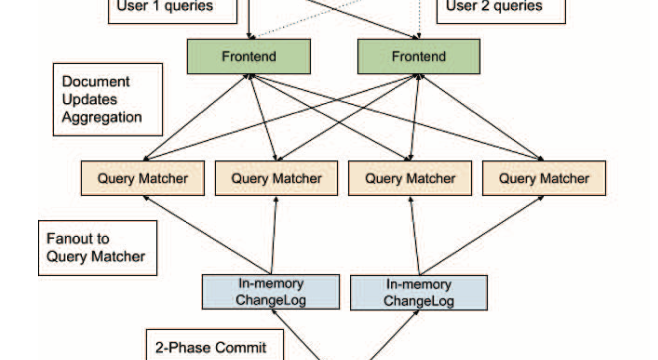
- What is new: This research investigates the suitability of NoSQL (Google Cloud Firestore) versus SQL (Cloud SQL MySQL) databases for powering the backend of a peer-to-peer energy marketplace for electric vehicle charging, introducing a GraphQL middleware layer as a novel solution to potential deficiencies.
- Why this is important: The expansion of electric vehicle infrastructure in underserved areas is limited by range anxiety, and existing charging solutions do not meet all needs.
- What the research proposes: A peer-to-peer energy marketplace that allows private owners to rent out charging facilities, utilizing Cloud-connected microcontrollers for security and session management.
- Results: The study finds that NoSQL databases, specifically Google Cloud Firestore, may be more suitable for this application due to better scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency, and that GraphQL can address any shortcomings.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Cloud-connected microcontrollers, web-based user interface for the marketplace
Models used: NoSQL (Google Cloud Firestore) vs SQL (Cloud SQL MySQL)
Data used: Query latency, flexibility/scalability, and cost criteria
Potential Impact
This research impacts the electric vehicle market, particularly companies involved in EV charging infrastructure, and can potentially disrupt traditional charging station providers by empowering private small-scale providers.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: ChargeMate.

Leave a Reply