Authors: Valentina Scarponi, Michel Duprez, Florent Nageotte, Stéphane Cotin
Published on: March 05, 2024
Impact Score: 7.6
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2403.02777
Summary
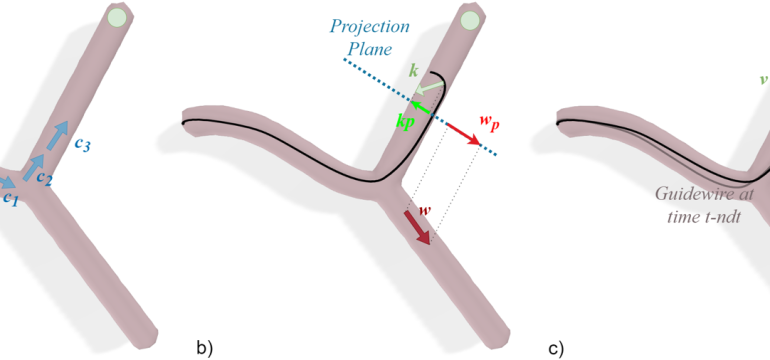
- What is new: A zero-shot learning strategy for 3D autonomous endovascular navigation capable of adapting to unseen vascular anatomies without retraining.
- Why this is important: Existing methods for the automated navigation of guidewires and catheters in cardiovascular interventions struggle with generalizing to new vascular geometries, necessitating frequent retraining.
- What the research proposes: A reinforcement learning algorithm that relies on a small training set of branching patterns to learn controls applicable to unseen vascular anatomies.
- Results: Achieved a 95% success rate at reaching random targets across 4 different vascular systems, with the entire training process taking only 2 hours.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Deep Reinforcement Learning
Models used: Zero-shot learning strategy
Data used: Small training set of vascular branching patterns
Potential Impact
The healthcare sector, particularly companies involved in cardiology and medical imaging, as well as manufacturers of robotics for surgical interventions.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: VascuNav.
Leave a Reply