Authors: Kenji Koide, Shuji Oishi, Masashi Yokozuka, Atsuhiko Banno
Published on: February 08, 2024
Impact Score: 8.15
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2402.05540
Summary
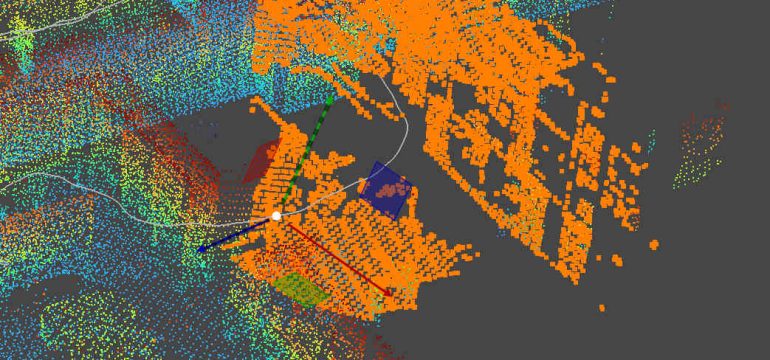
- What is new: A new algorithm for inertial localization that tightly couples scan-to-scan and scan-to-map registration with IMU data for improved tracking in challenging conditions.
- Why this is important: Existing localization methods struggle with severe point cloud degeneration, sensor interruptions, and navigating unmapped regions.
- What the research proposes: Tightly coupled scan-to-scan and scan-to-map registration factors with IMU factors, utilizing a sliding window factor graph for enhanced sensor pose tracking.
- Results: The proposed method surpasses current leading techniques, especially under extreme conditions such as degenerate point cloud data and sensor disruptions.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Sliding window factor graph
Models used: Scan-to-Scan and Scan-to-Map point cloud registration, IMU factors coupling
Data used: 3D prior maps, inertial measurement unit (IMU) data
Potential Impact
Autonomous vehicle navigation, augmented reality applications, mobile robotics, and companies specializing in mapping and spatial analytics technologies.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: PathfinderTech.



Leave a Reply