Authors: Prabhat Kumar, Michael Hoffmann, Andrew Nonaka, Sayeef Salahuddin
Published on: February 08, 2024
Impact Score: 8.22
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2402.05331
Summary
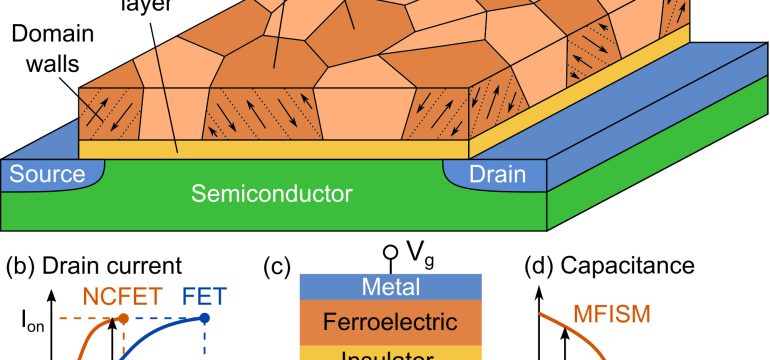
- What is new: This study uses 3D phase field simulations to explore the necessary conditions for negative capacitance (NC) stabilization in HfO2- and ZrO2-based ferroelectric thin films, focusing on the role of topological domain walls.
- Why this is important: There’s a gap in understanding the role of domain formation and motion, as well as anisotropic domain wall coupling, on negative capacitance in mixed-phase, polycrystalline ferroelectric thin films.
- What the research proposes: Applied 3D phase field simulations to identify conditions favoring NC stabilization in HfO2- and ZrO2-based ultra-thin films, emphasizing grain size, polar axis orientation, and domain wall coupling.
- Results: Identified conditions that enhance NC effect include smaller ferroelectric grains and a larger polar axis angle to the plane. It also finds that negative domain wall coupling along any axis prevents NC stabilization, highlighting the importance of topological domain walls.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: 3D phase field
Models used: Simulations of HfO2- and ZrO2-based mixed-phase ultra-thin films
Data used: Properties and behaviors of HfO2- and ZrO2-based ferroelectrics
Potential Impact
Semiconductor industry, specifically companies developing or using next-generation electronic devices with gate oxides, e.g., microprocessor manufacturers, memory storage device makers.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: NanoCapTech.

Leave a Reply