Authors: Seungjun Lee, Hyeong-Ryul Kim, Wei Jiang, Young-Kyun Kwon, Tony Low
Published on: February 06, 2024
Impact Score: 8.15
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2402.04387
Summary
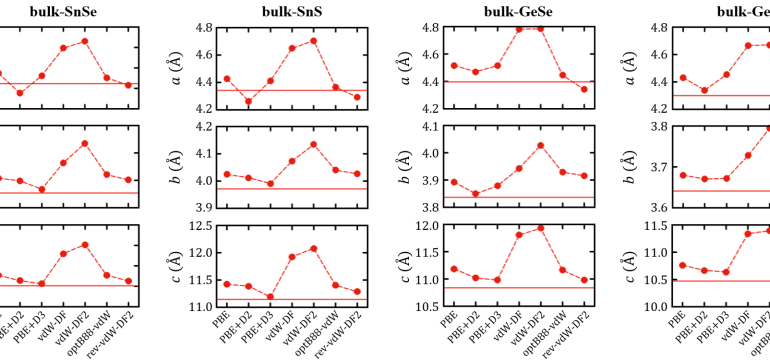
- What is new: The discovery that AA-stacked MXs with ferroelectric ground state exhibit a giant piezoelectric coefficient that increases with layer number.
- Why this is important: Existing group IV monochalcogenides lose piezoelectricity with increasing layer number due to antiferroelectric stacking.
- What the research proposes: Investigating piezoelectricity in MXs with ferroelectric AA stacking configuration, which shows increased piezoelectric coefficients with more layers.
- Results: AA-stacked MXs demonstrated a giant piezoelectric coefficient thanks to a strong negative correlation between lattice constant and piezoelectric coefficient and spontaneous compressive strain in the ferroelectric AA stacking.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: First-principles calculations
Models used: Piezoelectric coefficients analysis
Data used: Group IV monochalcogenides (MXs)
Potential Impact
Companies in electronics, sensors, and actuators markets could benefit, while traditional 2D materials might face disruption.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: FlexiCharge.

Leave a Reply