Authors: Diptyaroop Maji, Noman Bashir, David Irwin, Prashant Shenoy, Ramesh K. Sitaraman
Published on: February 05, 2024
Impact Score: 8.2
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2402.03550
Summary
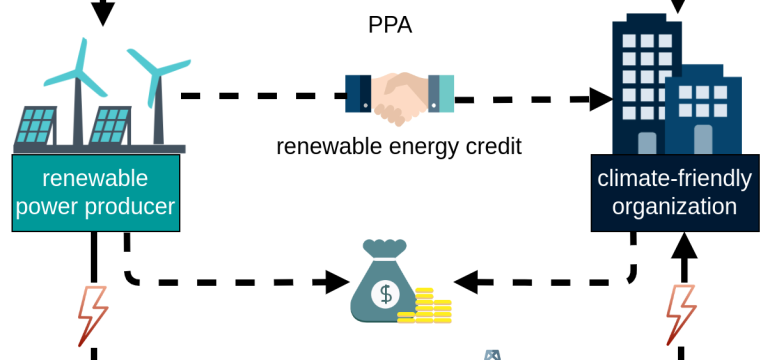
- What is new: This paper reveals discrepancies in carbon savings reported by existing carbon optimization techniques due to the concurrent use of location-based and market-based methods for attributing renewable energy credits.
- Why this is important: There’s a lack of consensus on the method for attributing carbon-free energy, causing discrepancies in carbon savings reports.
- What the research proposes: The study analyzes the effects of concurrent attribution methods on carbon savings and suggests a reevaluation of these methods.
- Results: Up to 55.1% overestimation in carbon reductions using current methods, with the market-based method yielding up to 28.2% less carbon savings for consumers without PPAs.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: nan
Models used: State-of-the-art carbon optimization techniques
Data used: Data on carbon intensity across regions, and information from power purchase agreements.
Potential Impact
Energy sector, carbon information services, companies with sustainability goals, renewable energy markets.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: EcoNex.

Leave a Reply