Authors: Jinyang Li, Timothy Kovachy, Jason Bonacum, Selim M. Shahriar
Published on: February 06, 2024
Impact Score: 8.3
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2402.03608
Summary
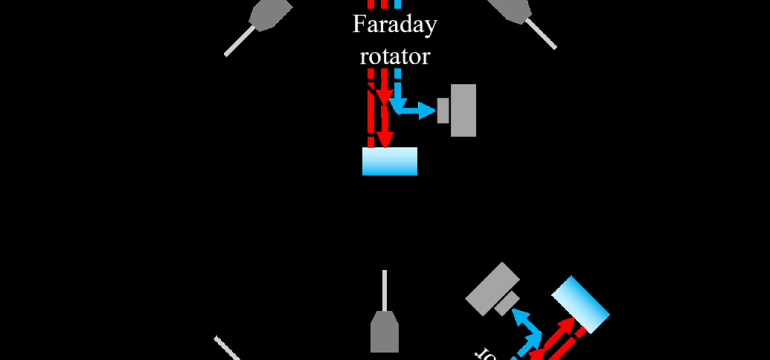
- What is new: Introduces a point-source interferometer method using molasses-launched atoms for accelerometry and rotation sensing that simplifies the apparatus and reduces measurement time.
- Why this is important: Existing methods for measuring acceleration and rotation with interferometers are complex and time-consuming.
- What the research proposes: Employing large momentum transfer with molasses-launched atoms without needing to physically change the Raman pulses’ directions.
- Results: Outlined a scheme for an inertial measurement unit (IMU) with expected sensitivity and bandwidth improvements.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Point-source interferometer with molasses-launched atoms for LMT
Models used: Theoretical analysis of sensitivity and bandwidth for the proposed IMU
Data used: Experimentally accessible parameters for sensitivity and bandwidth estimations
Potential Impact
Aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries; companies developing or relying on IMUs and navigation technology.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: QuantumNav.


Leave a Reply