Authors: Yasmine Kalboussi, Baptiste Delatte, Sarra Bira, Kassiogé Dembele, Xiaoyan Li, Frederic Miserque, Nathalie Brun, Michael Walls, Jean-luc Maurice, Diana Dragoe, Jocelyne Leroy, David Longuevergne, Aurélie Gentils, Stéphanie Jublot-Leclerc, Gregoire Julien, Fabien Eozenou, Matthieu Baudrier, Luc Maurice, Thomas Proslier
Published on: February 06, 2024
Impact Score: 8.38
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2402.04137
Summary
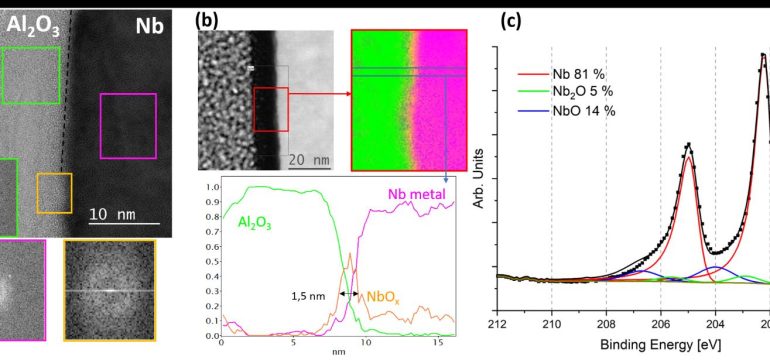
- What is new: Demonstration of reduced two-level system losses in superconducting qubits by applying a novel method involving atomic layer deposition of aluminum oxide and subsequent heat treatment.
- Why this is important: Quantum coherence lifetimes in superconducting qubit circuits are limited by dissipations caused by two-level system defects.
- What the research proposes: Applying a 10 nm aluminum oxide layer on niobium resonators followed by high vacuum heat treatment at 650 °C to enhance quantum coherence lifetimes.
- Results: Enhancement of the quality factor at low fields in two 1.3 GHz niobium cavities coated with 10 nm of Al2O3, indicating improved computational reliability of qubit circuits.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Atomic layer deposition (ALD), high vacuum (HV) heat treatment
Models used: X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning and high resolution transmission electron microscopy (STEM/HRTEM), electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX)
Data used: Probing effects on Al2O3-coated niobium samples
Potential Impact
Quantum computing platforms, semiconductor manufacturing, and companies investing in the production of superconducting qubits.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: QuantBoost.

Leave a Reply