Authors: Mario A.V. Saucedo, Akash Patel, Akshit Saradagi, Christoforos Kanellakis, George Nikolakopoulos
Published on: February 06, 2024
Impact Score: 8.22
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2402.03840
Summary
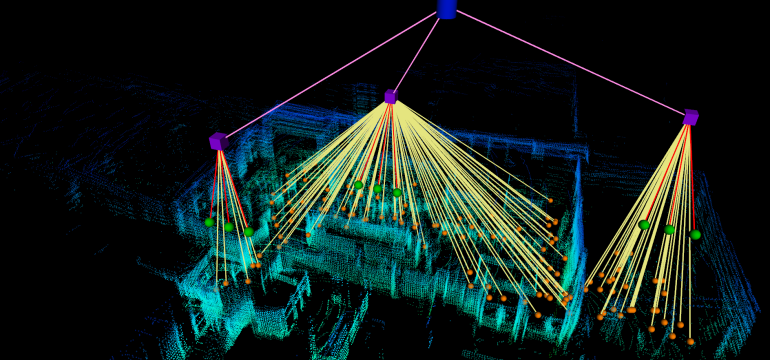
- What is new: Introduction of Belief Scene Graphs (BSG) for efficient high-level task planning in robotics with partial information.
- Why this is important: The challenge of task planning in robotics with incomplete 3D information.
- What the research proposes: A graph-based learning method called Computation of Expectation based on Correlation Information (CECI) for approximating real belief on 3D scene graphs.
- Results: The CECI model, trained on a novel dataset of 3D scene graphs, effectively enables robots to plan tasks by integrating expectations into abstract representations.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: Graph Convolutional Neural Network (GCN)
Models used: CECI model for learning from 3D scene graphs.
Data used: A new dataset of 3D scene graphs generated from semantically annotated real-life 3D spaces.
Potential Impact
Robotics, autonomous vehicles, augmented reality companies, and markets could significantly benefit or face disruption from these insights.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: GraphSense.


Leave a Reply