Authors: Gabriel Ioan Arcas, Tudor Cioara, Ionut Anghel, Dragos Lazea, Anca Hangan
Published on: January 15, 2024
Impact Score: 8.22
Arxiv code: Arxiv:2402.01664
Summary
- What is new: This paper explores the adoption of edge offloading in smart grids to address the challenges of low latency and high-reliability required by new data-driven applications.
- Why this is important: Traditional cloud-based smart grid architectures cannot meet the low latency and high-reliability requirements of emerging smart grid applications.
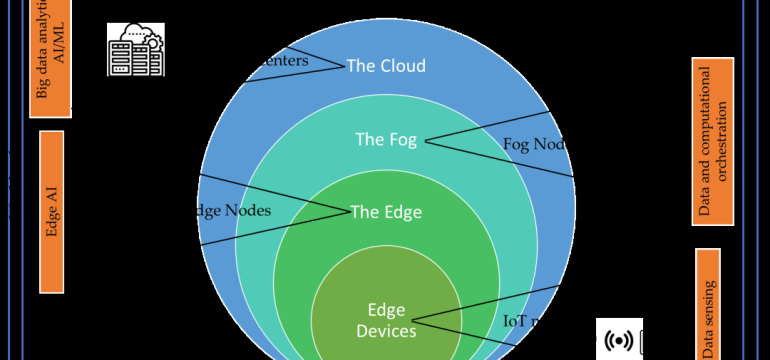
- What the research proposes: The paper investigates alternative architectures like edge, fog, or hybrid and edge offloading to improve computing resource utilization and optimize response time, energy consumption, and network performance.
- Results: A SWOT analysis and an evaluation of decision-making variables and optimization algorithms are provided, demonstrating the efficiency of edge offloading for smart grids.
Technical Details
Technological frameworks used: edge-fog-cloud models, orchestration architecture, serverless computing
Models used: optimization algorithms
Data used: data generated by IoT devices in smart grids
Potential Impact
Energy sector, smart grid technology companies, IoT device manufacturers, cloud service providers might be affected, with potential benefits for startups focused on edge computing solutions for smart grids.
Want to implement this idea in a business?
We have generated a startup concept here: GridFlex.

Leave a Reply